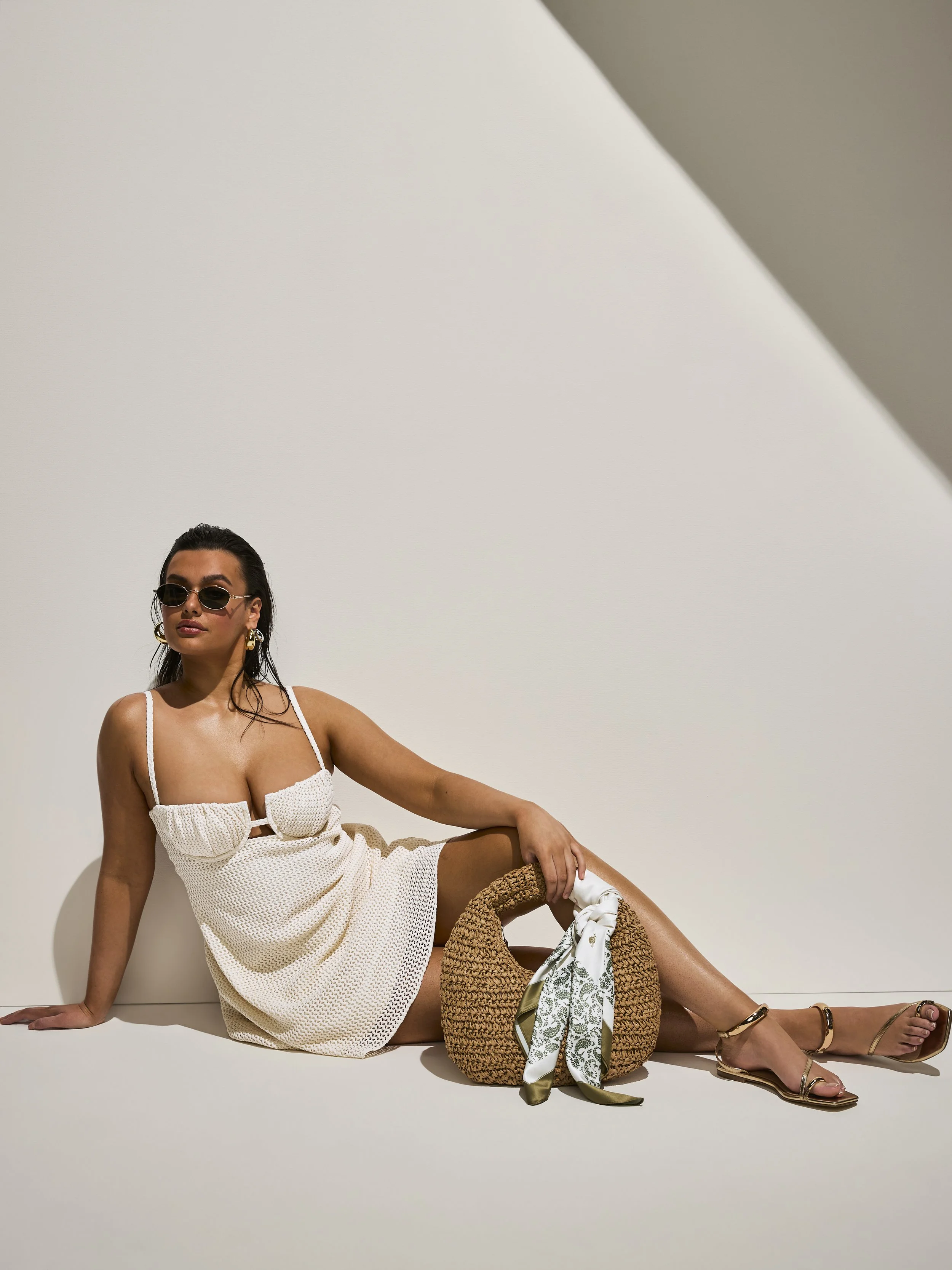
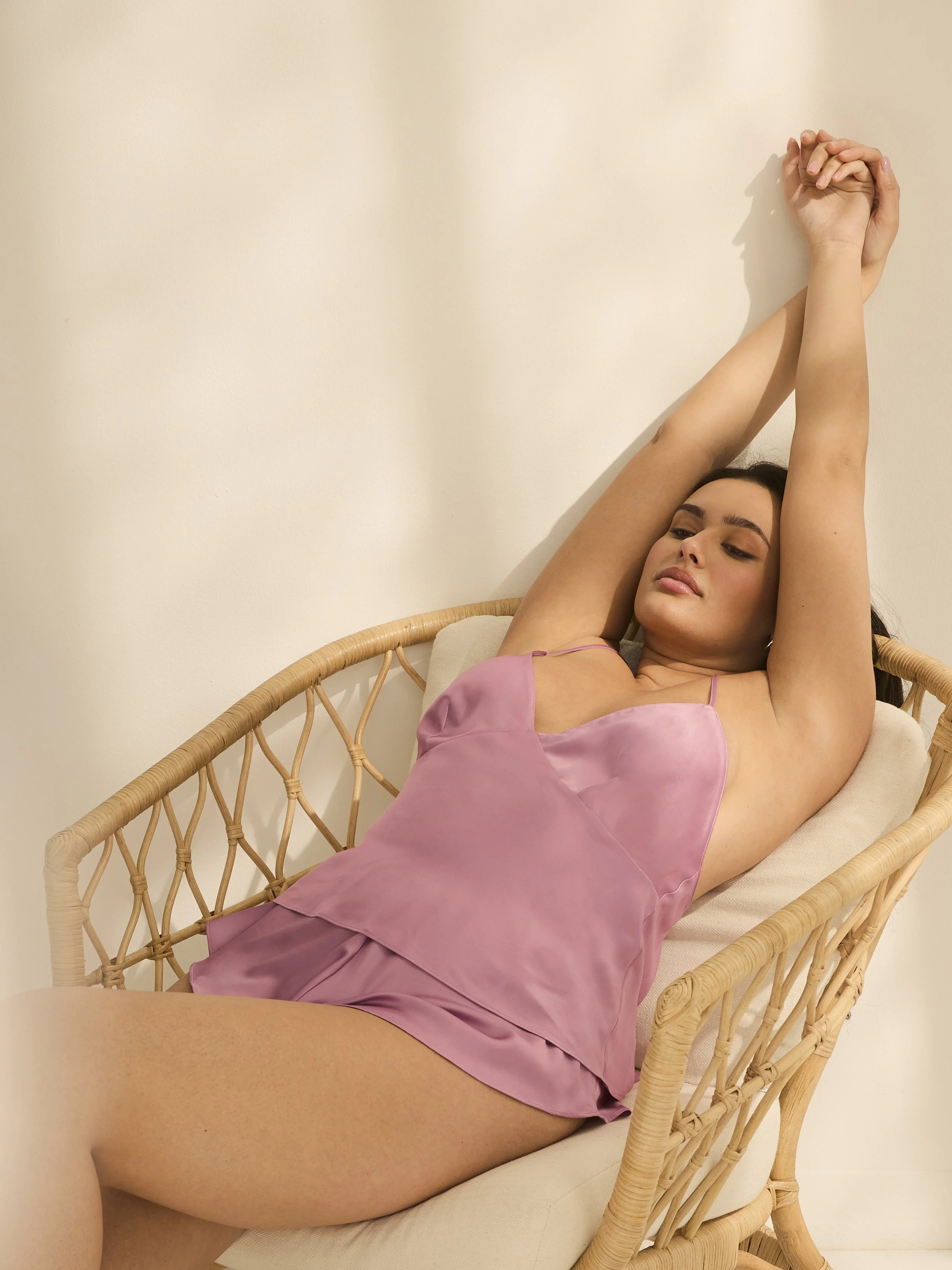
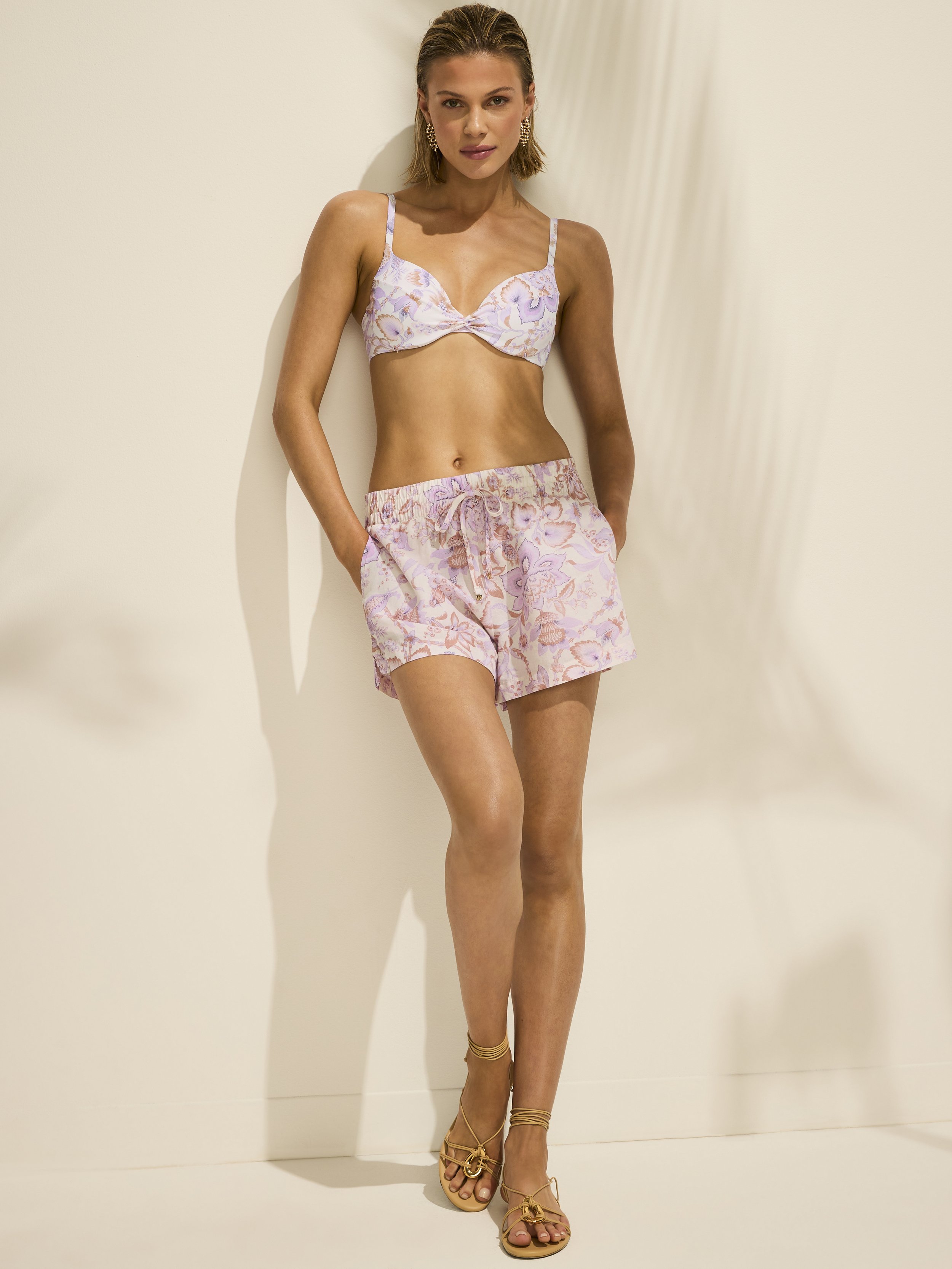
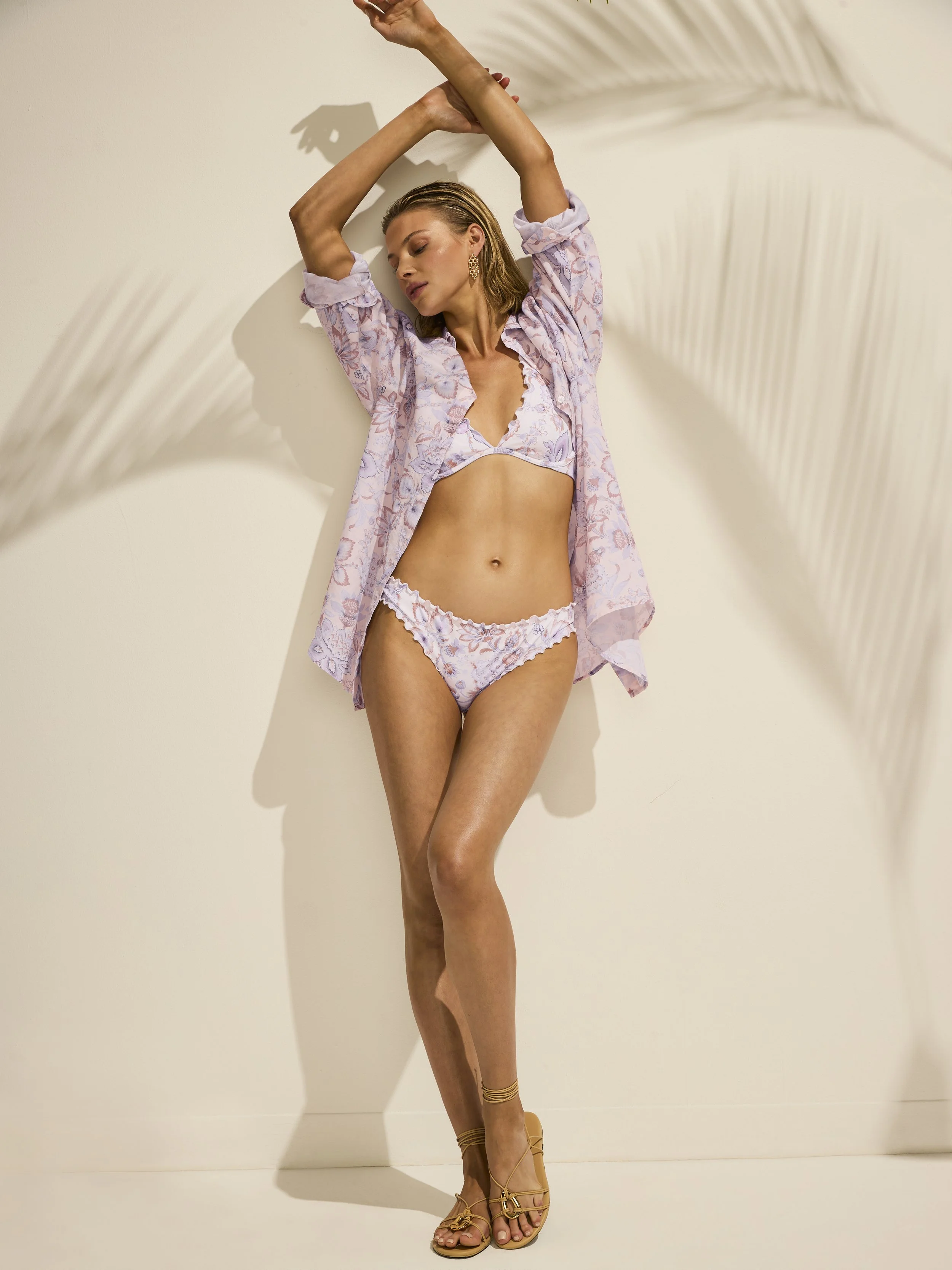
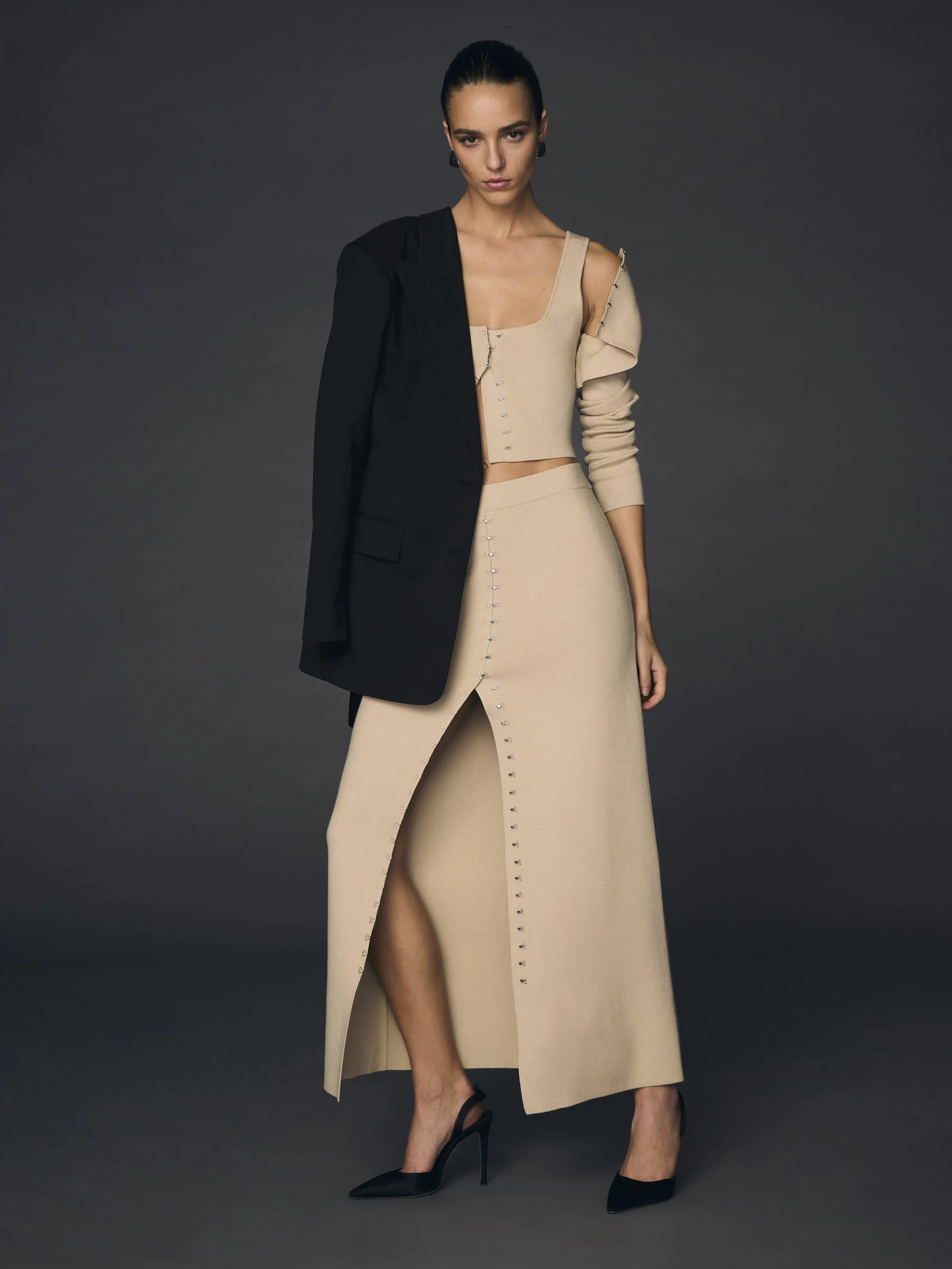
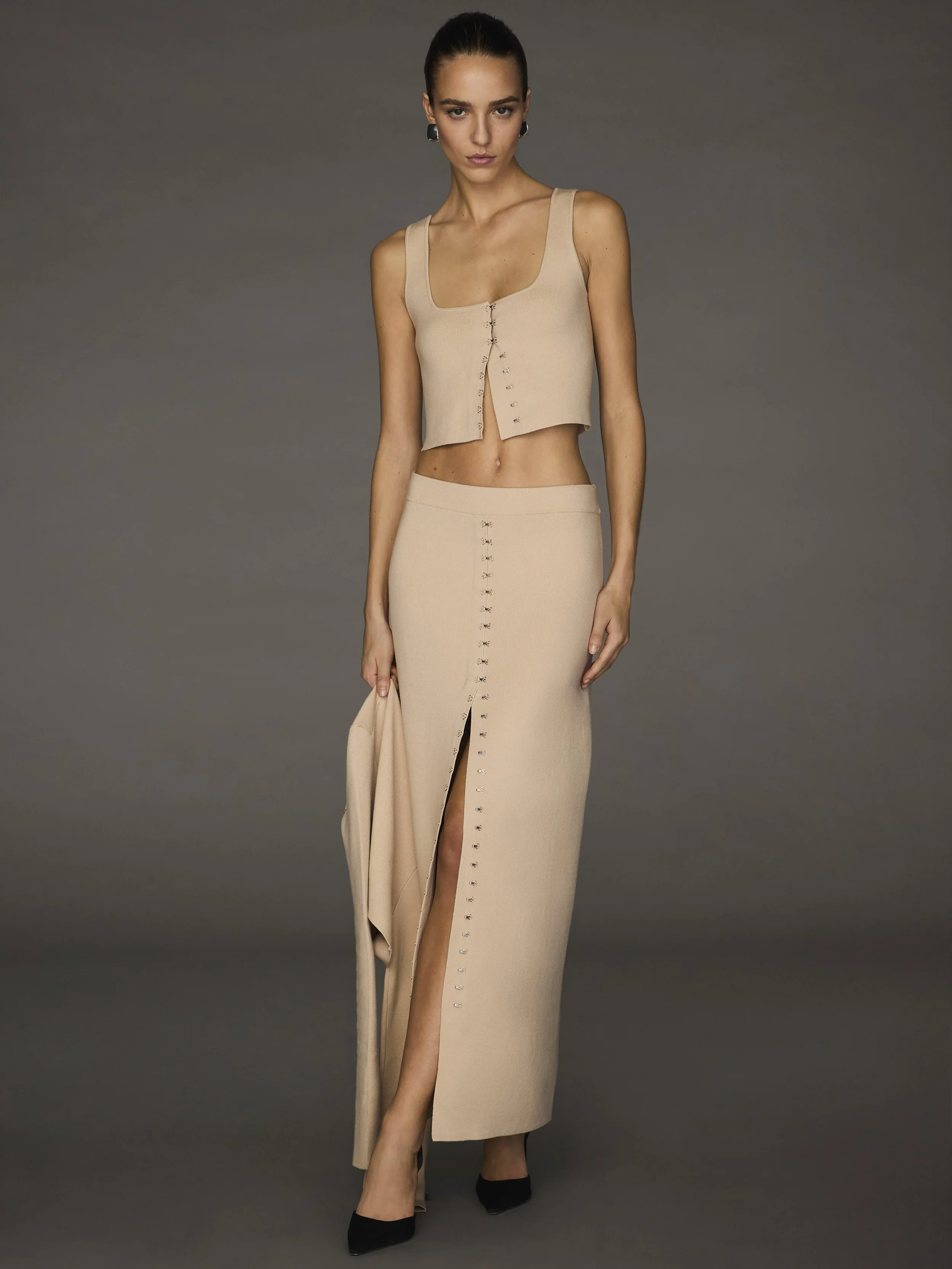
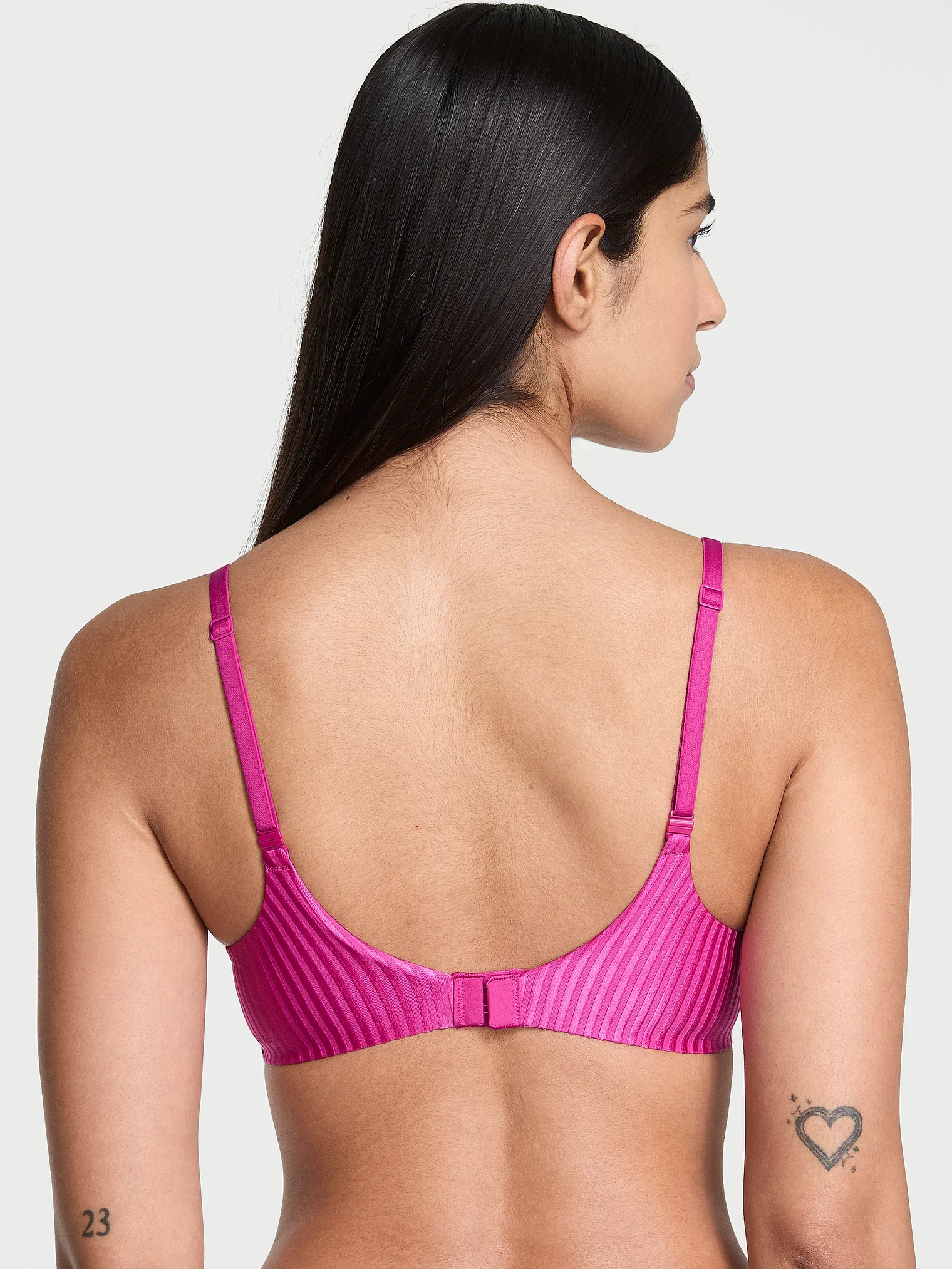
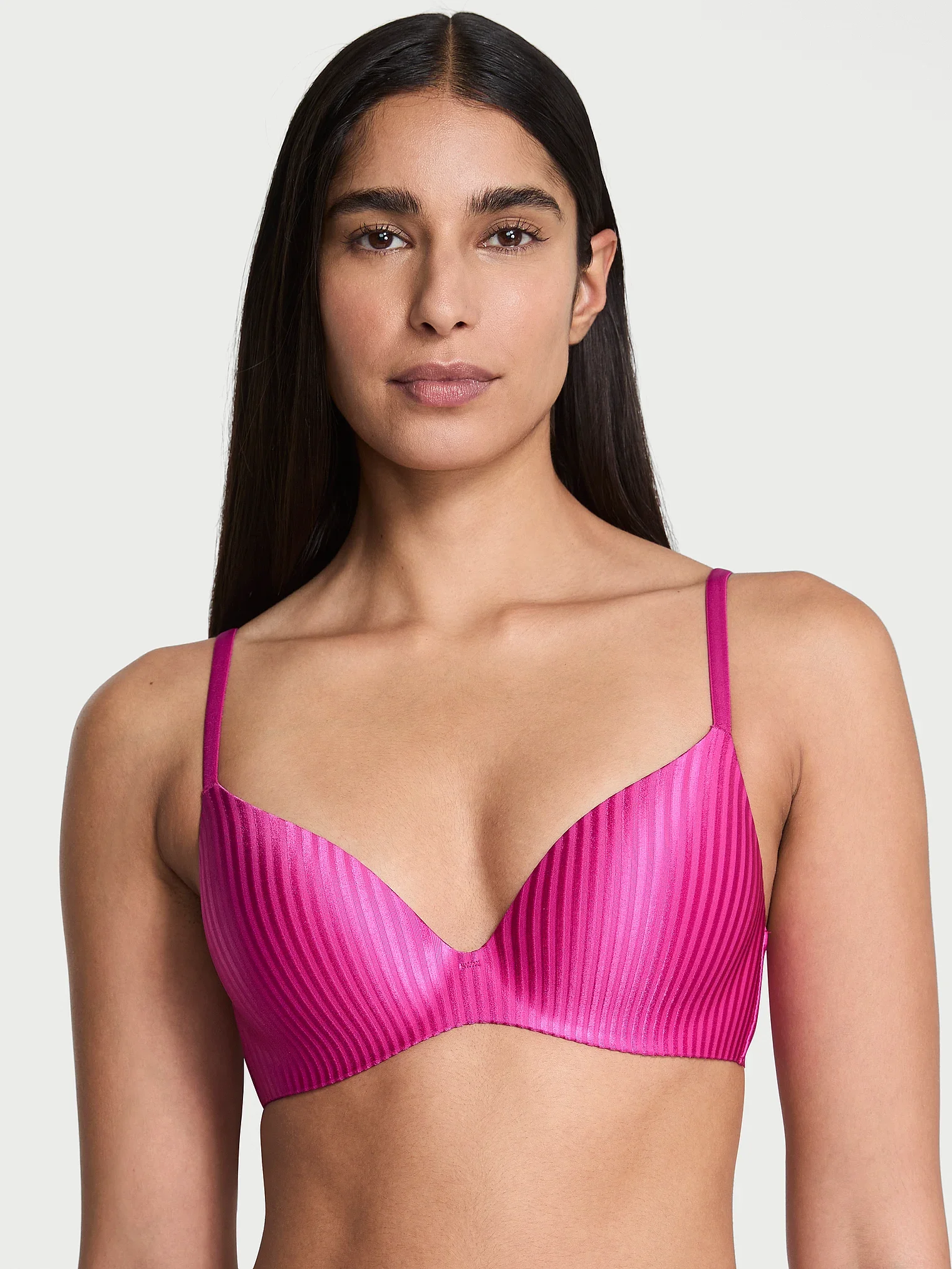
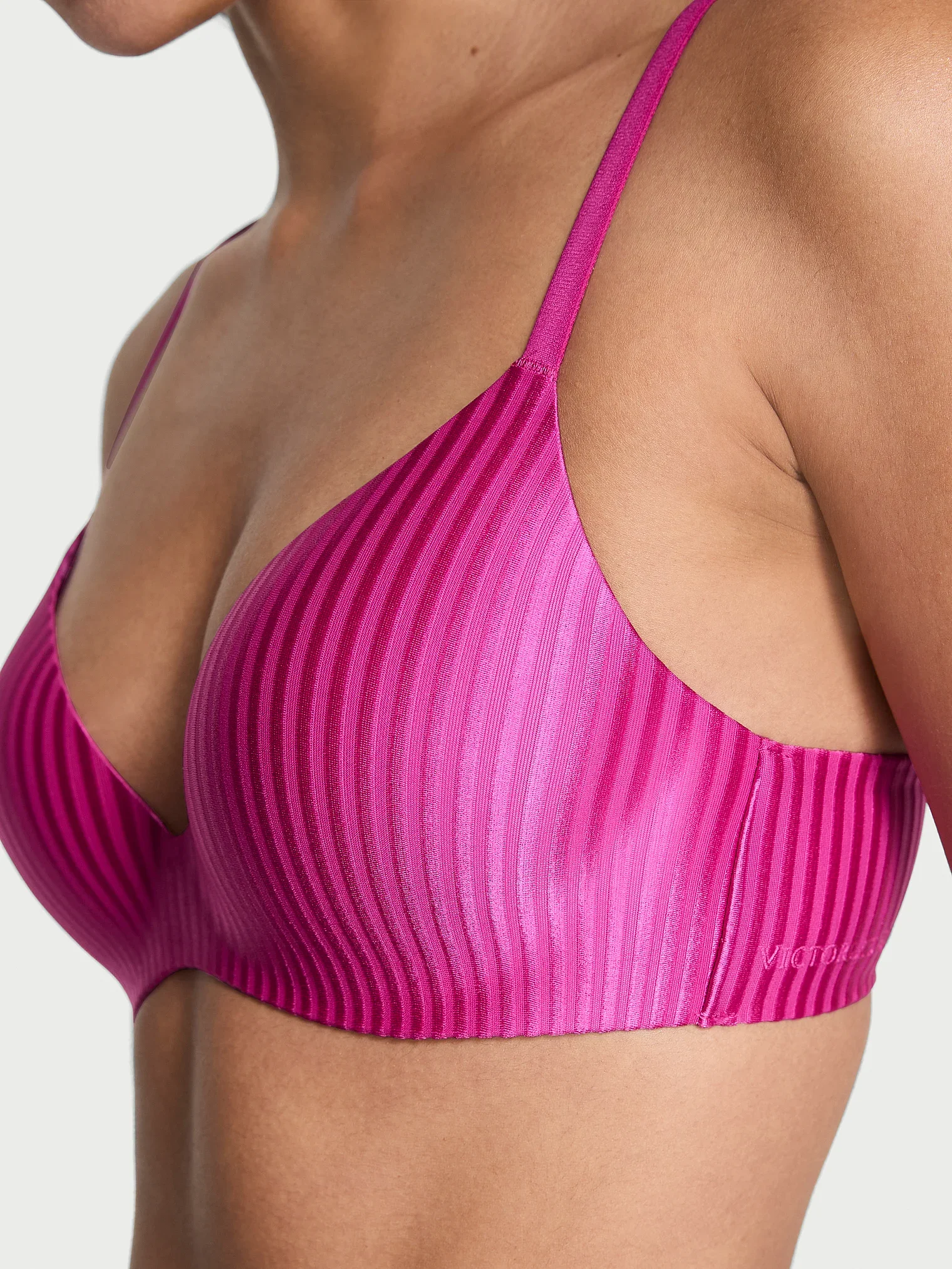
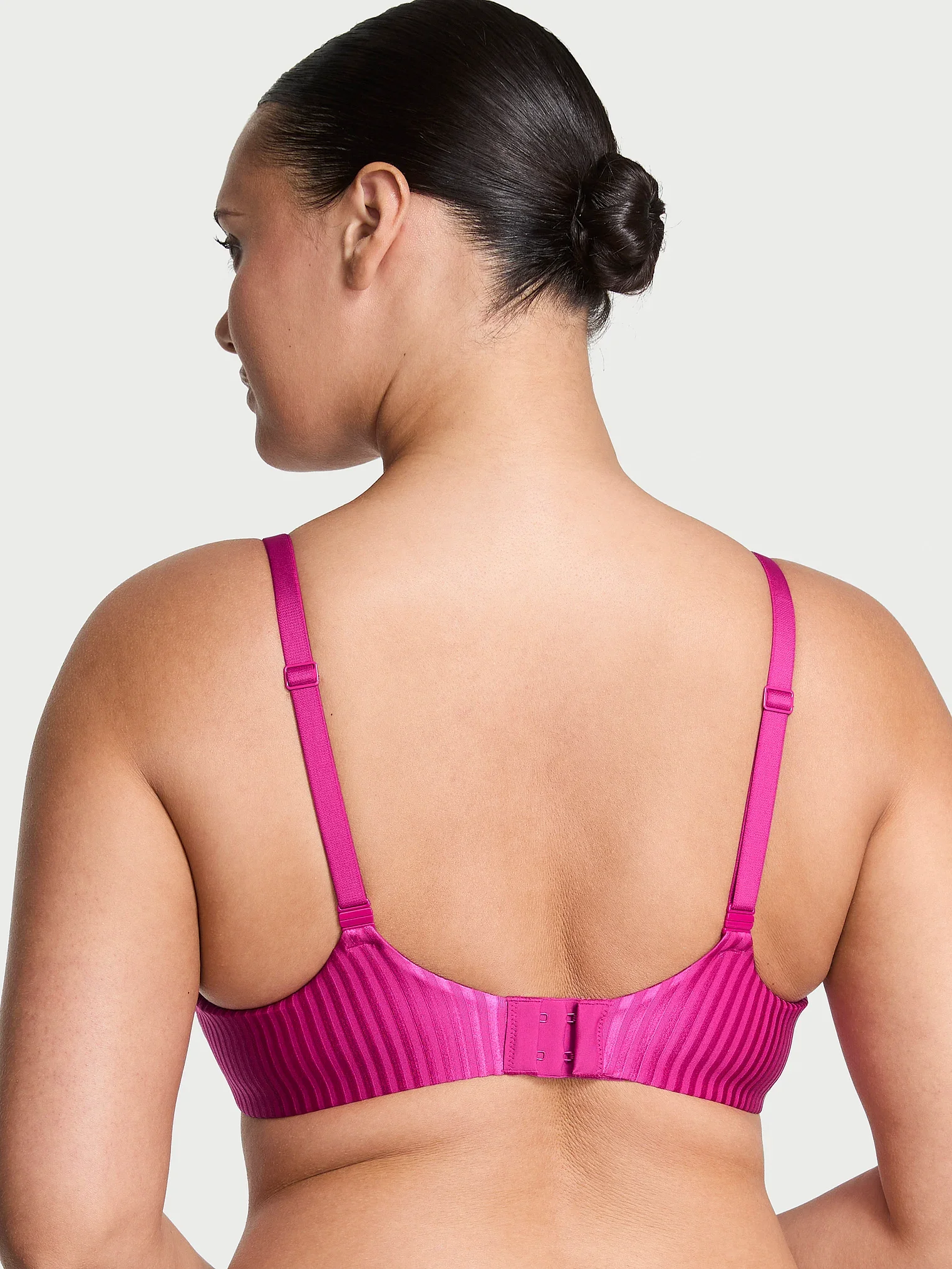
Post Production Management
Creative Services Lead with 17 years of extensive expertise in quality control, operations strategy and cloud-based systems
Elevated PDP
Elevated PDP
Atelier Victoria's Secret x Altuzarra
Elevated PDP - LSFxPINK
PDP
Editorial
Stills- Beauty
Stills- Accessories
Stills- Laydowns

E-Comm Process
Quality assurance opportunities leveraged at every point
PRE-PRODUCTION
Goal: Plan and organize all creative assets needed to execute a smooth production cycle.
QA Enhancement Strategies:
Creative Briefing
- Define clear expectations and success criteria. QA begins early and with clarity; solid briefs prevent misalignment later. Include brand standards, image usage requirements, and visual tone guidelines.Product Intake & Sample Management and Metadata
- Implement intake checklists to verify SKU numbers, condition, and completeness. Barcode scanning and intake logs ensure traceability and reduce lost or incorrect product issues,Style Guide Review / Create Ops & Post Lead SOP Development
- Align all teams on style expectations. Update visual style guides and SOPs to include QA checkpoints. Use version-controlled documents and train teams on changes.Shot List Creation and Product Data QC
- Audit shot lists for completeness and accuracy against product data. Cross-reference PDP requirements to ensure no missing angles or data misalignment.Talent / Model Booking (if needed)
- Use vetted talent pools and QA model cards (model look books) to match casting to brand guidelines. Secure proper usage rights documentation and legal clearance.Scheduling & Resourcing
- Build in QA buffer time during planning. Resource allocation should include QA reviewers at appropriate steps, not just production roles.Set Design / Prop Prep
- QA materials and props for brand compliance and fit. Create checklists for cleanliness, color correctness, and consistency with the brief. Prop barcodes that are aligned with brand resources
PRODUCTION
Goal: Capture all required imagery per creative brief and e-commerce standards.
QA Enhancement Strategies:
Studio Setup & Calibration
- Daily equipment calibration (color cards, light balance, monitor settings) ensures consistent image quality. Maintain setup logs and checklist sign-offs.Styling & Product Prep
- Implement styling SOPs for each category (folding, steaming, stuffing, pinning). Assign styling QA leads to check before shoot starts.Photography
- real-time QA review. Set exposure, color balance, and angle tolerances. Create lightening diagrams and Lock in camera settings to avoid inconsistency.- Art directors to monitor adherence to the brief and correct issues live. Implement a “shoot-stop” protocol for major deviations.
File Compliance, Transfer & Backup
- Validate file format, naming conventions, and folder structures before transfer. Use checksum verifications or automated transfer tools to prevent loss or corruption.
POST-PRODUCTION
Goal: Road map, refine, approve, and deliver assets optimized for e-commerce platforms.
QA Enhancement Strategies:
Review of Captured Images, Image Selection, Retouching Markups
- QA ensures selected images meet visual standards, focus, and brand guidelines. Use markup tools for standardized retouching notes.Retouching & Color Correction
- Establish QA workflows using reference color profiles and before/after comparison tools. Employ tiered reviews (junior to lead).Digital Twin, CGI
- QA 3D outputs for accuracy in dimensions, textures, and lighting. Use real product comparisons and rendering benchmarks.QA & Brand Compliance Review
- Final QA pass includes checks for logo visibility, brand colors, product representation accuracy, and brand compliance.Cropping, Resizing, Naming, Colorways, Pickups
- Automate cropping and resizing with scripts where possible. Validate output naming against SKU databases and ensure all product variations are accounted for.Upload to DAM / CMS
- Audit uploads for metadata accuracy, proper tagging, and correct versions. Employ duplicate detection and automated status reporting.Delivery to E-Comm Platforms
- Test file delivery formats (web optimized, RGB vs CMYK). Use test uploads to validate final product visibility and formatting on front-end platforms.
FEEDBACK & CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
Goal: Ensure process learning and systemic refinement through data, tools, and team engagement.
QA Enhancement Strategies:
Stakeholder Review & Feedback
- Create structured review templates to capture actionable QA insights. Hold post-mortems to assess what worked and what didn’t.Metrics & Reporting
- Implement dashboards to track revision rates, error types, and turnaround times. Use KPIs to surface QA trends and team performance.SOP Refinement
- Regularly audit SOPs for gaps found during production. Use versioning and maintain change logs. Align updates with training refreshers.Automation Development
- Reduce manual errors by scripting repetitive QA tasks like file checks, color, background verification and metadata validation.Consolidation of Tech Stack and Tools
- Evaluate tool effectiveness in supporting QA. Sunset redundant or error prone tools.Adhoc and Invisible Work Assessments
- Use QA feedback loops to uncover hidden effort or frequent fire drills. Track these “invisible” issues and create proactive prevention plans.Studio Audits and Evaluation of the 5S
- Conduct regular audits using the 5S framework (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) to ensure cleanliness, efficiency, and standard adherence; all contributing to fewer quality issues.

Scalable Creative
How to Create Scalable E-commerce Creative on demand Through SOPs
True scalability in e-commerce creative production means maintaining consistent quality and brand alignment while dramatically increasing output volume—all without exponentially expanding your team or budget. SOPs form the strategic foundation that makes this transformation possible.
Core Principles
1. Standardization
Define clear guidelines for every aspect of creative production: naming conventions, brand compliance, file organization, and output formats across all channels, these should be created as flattening scripts.
2. Build on Existing Infrastructure
Leverage current workflows and systems. Identify successful patterns and expand their application across new creative verticals and team structures.
3. Modular Templates
Create a comprehensive library of reusable templates for all common formats and organize them systematically—they don't need to be brand-specific. For example, you might have a post workflow for product stills with a grounding shadow and white background. This way, different background colors can be edited into new workflows that reference the already established template, making it easy to adapt while maintaining consistency.
4. Strategic Automation
Automate repetitive, high-volume tasks using software and scripts. Focus on low-complexity activities that consume disproportionate resources.
5. Flexible Workflows
Design processes that accommodate growth. Build workflows with capacity for additional automation layers and team expansion without system overhauls.
Color Accuracy
Getting Colors Right: Keeping Your Brands Looking Sharp
Keeping your brand's colors spot on isn't just a nice to have; it's important for making sure everything looks consistent, no matter where it shows up. We want to avoid anyone just "eye-balling" colors and instead set up some solid rules for how we handle them.
All Your Colors in One Place
To keep things organized and with different people seeing colors differently, we need to gather all our approved colors in a central spot. These files should be tucked away in a safe, easy to get to place and, once approved, set to read-only. That way, no one can accidentally adjust them. And when we do need to tweak colors (like with adjustment layers or fills), we'll follow a set process every time.
Go-To Color Guides
• Color Hero (The "Perfect" Image): This is the gold standard for a specific color. It's an image that's been perfectly color-calibrated and approved. Every production file that uses this color should match its Color Hero exactly. We can even bake in color adjustments right into the Color Hero file, which is helpful for things like product shots where the lighting is usually pretty consistent. Plus, dedicated color layers within the approved file can act as a starting point for that color.
• Color Swatch (How Color Acts in Different Light): This is a photo of our approved color on the actual material it'll be used on (like fabric), showing both shadows and highlights. This gives us a great idea of how the color behaves when the lighting changes. We can keep these swatches in a "Reference" folder within the file. They're optimized to be small, so they won't bog down our files or servers.
• Color Chip (Solid Color & Digital Info): This is a simple representation of the solid approved color, and it can even include its RGB values. We can even set this up so it automatically pops into a fill layer in any file that uses that color's metadata. However, trying to perfectly match color chips to physical materials, especially textured ones or those with tricky lighting, can be challenging. For the best accuracy, it's smart to lean on industry standards like Pantone colors or their digital versions.